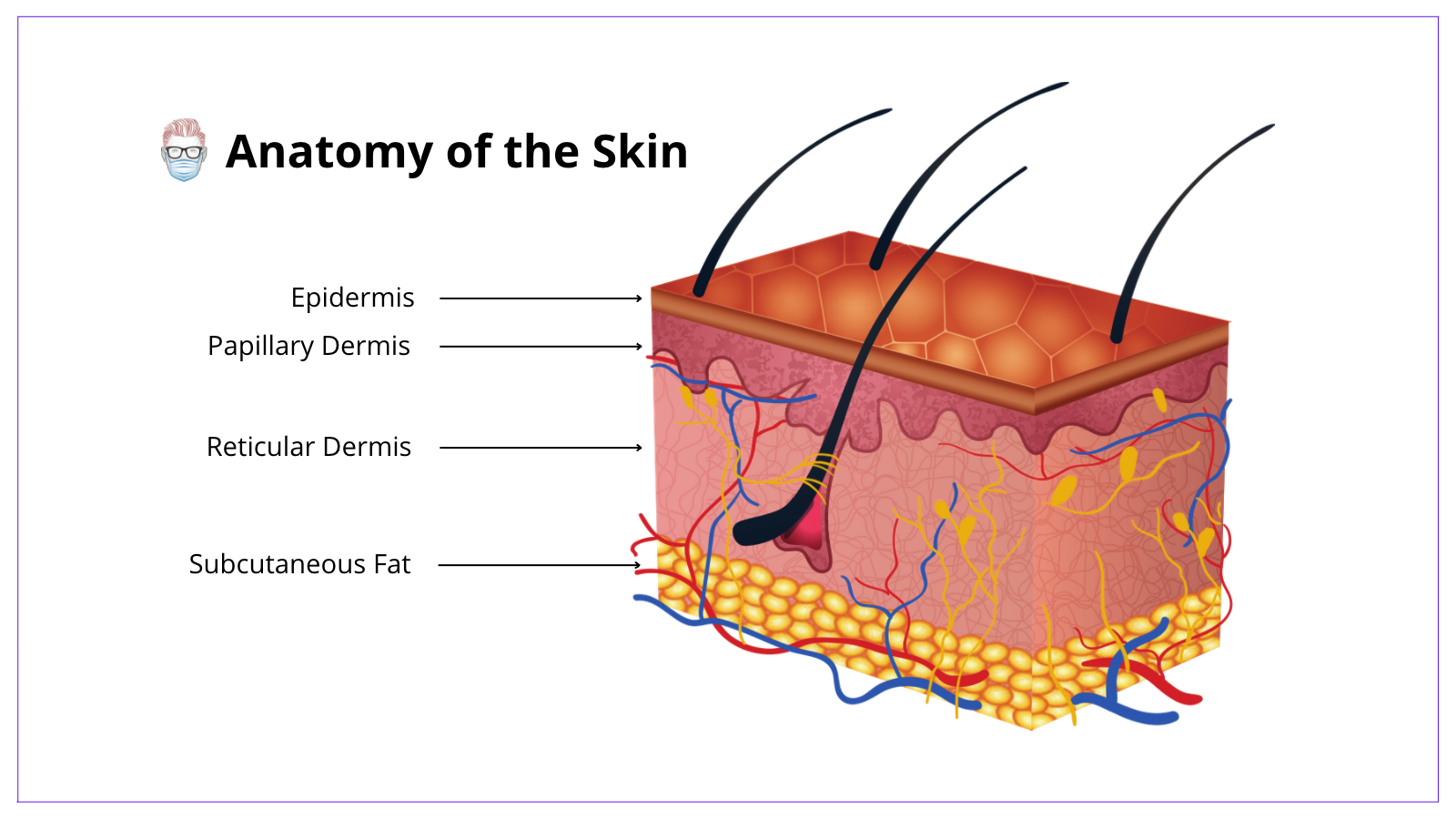
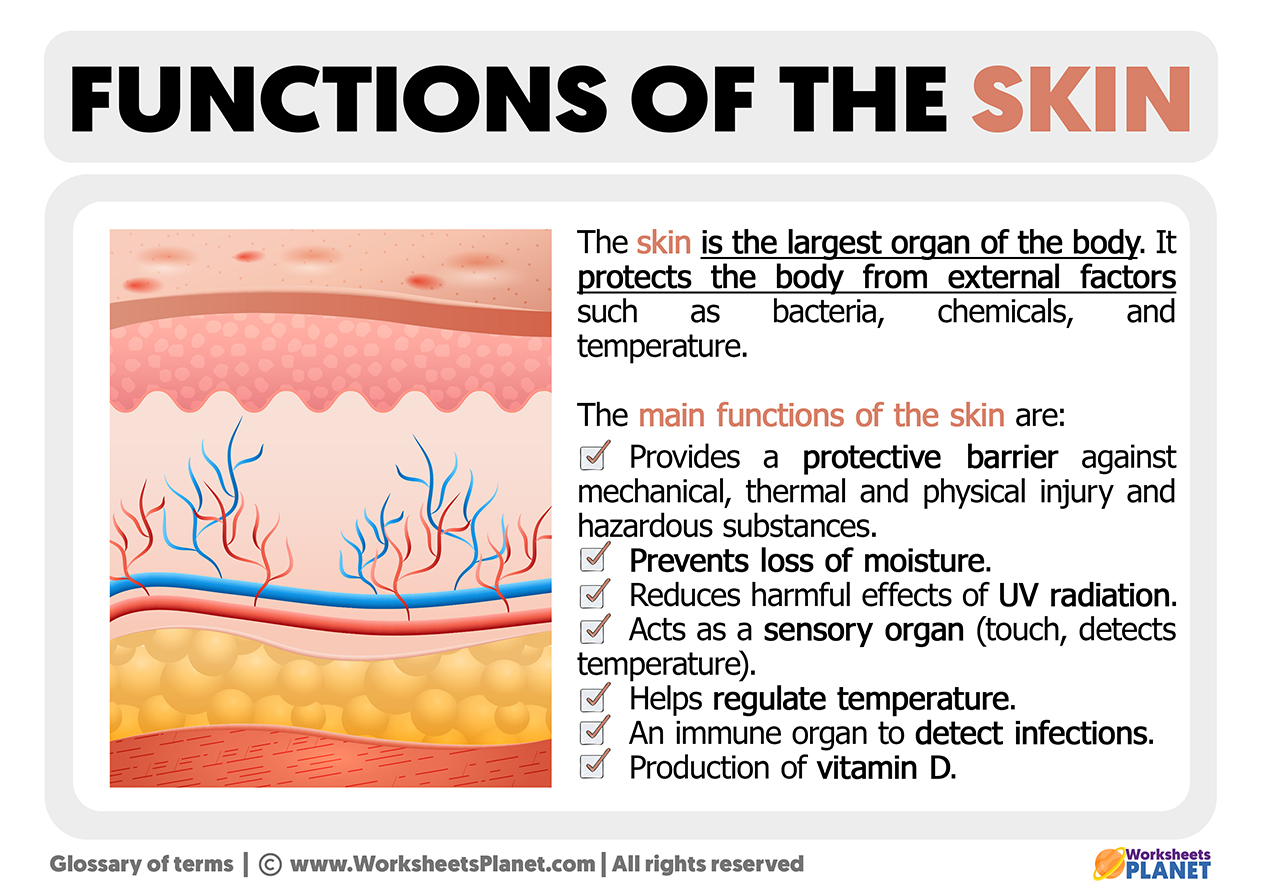
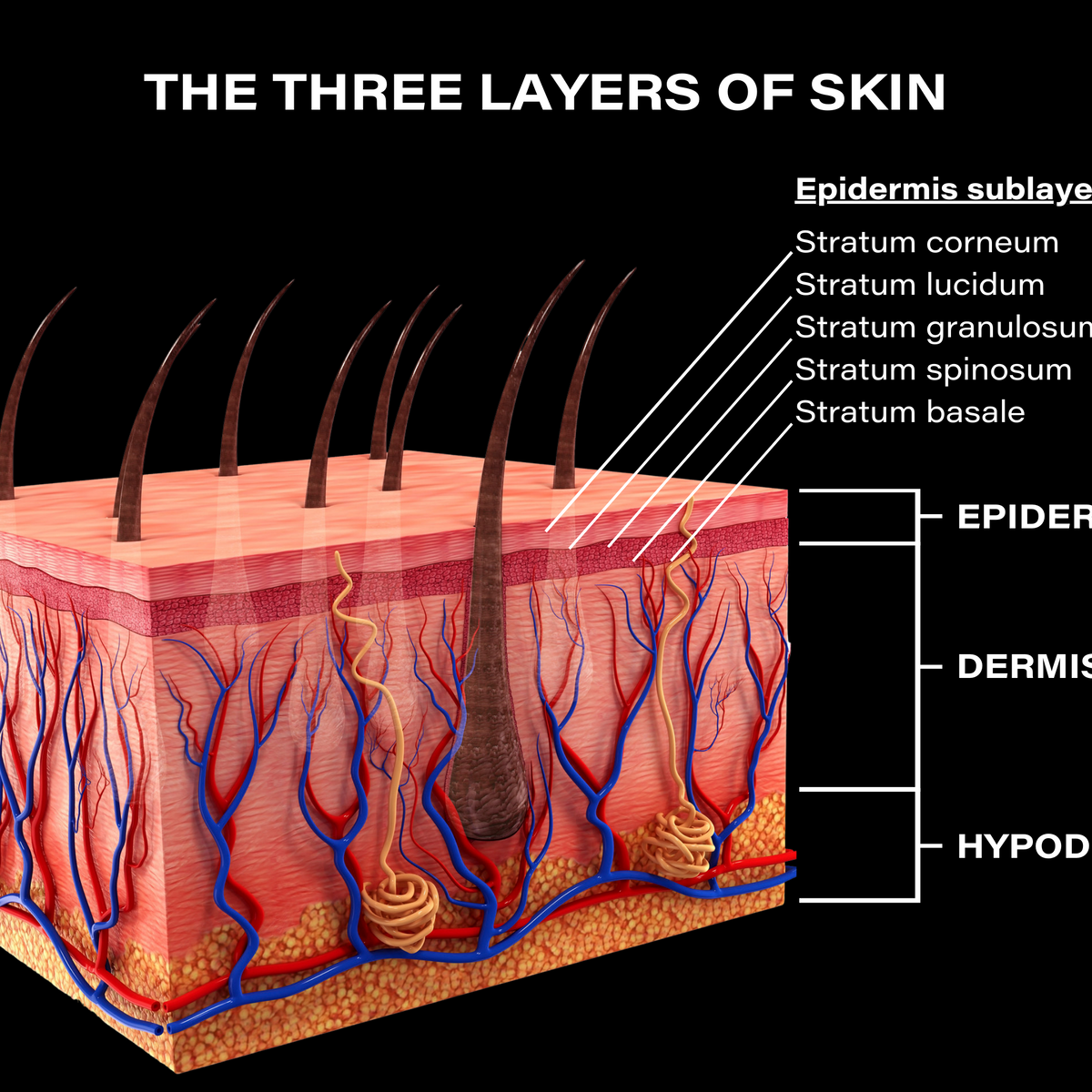
Scientists have identified dozens of genes that control melanin production, with some … Understand the complexities of skin color variations, why they occur, and comprehensive strategies for addressing changes in pigmentation. As embryos develop, they migrate to the epidermis and follicles and pigment the skin and hair. Melanocytes are neuroectoderm-derived pigment-producing cells with dendritic morphology. Hypopigmentation refers to patches of skin that are lighter than your natural skin tone due to reduced melanin (skin pigment) production. · tiny changes in your dna can have enormous effects on your skin’s appearance and function. Melanin synthesis occurs in a … This unit is dynamic and reactive to intrinsic … · hypopigmented macules are one of the most common skin lesions encountered in clinical practice. While it isnt a disease itself but a symptom of an underlying … · each melanocyte forms a functional and structural unit in human skin with 30–40 keratinocytes, known as the epidermal melanin unit. Melanocytes are specialized cells of the epidermis and hair follicle whose primary function is to synthesize and transfer melanin to adjacent keratinocytes. Among those, melanins play key roles in determining human … Melanocytes of the epidermis and hair are cells sharing some common features but in general they form biologically different populations living in unique niches of the skin. The word hypopigmentation indicates decreased pigmentation, which means … Pigments that determine human skin colors include melanin, hemoglobin (red), hemosiderin (brown), carotene (yellow), and bilin (yellow).
Skin Changes Explained The Medical Term For Less Melanocyte Activity
Scientists have identified dozens of genes that control melanin production, with some … Understand the complexities of skin color variations, why they occur, and comprehensive...